Harnessing potential of biological CO2 capture for Circular Economy
The objective of the CooCE project is to establish biotechnological processes, for converting CO2 into upgraded biofuels (biomethane) for on-site hybrid energy storage and value-added platform chemicals (biosuccinic acid (BioSA)) and biopolymers. The process involves fermentative technology that microbiologically couples biomass-derived sugars with CO2 to formulate bioSA. The project is in accordance with the European sustainable development goals considering circular bioeconomy. The consortium consists of DTU as technology provider, Lemvig Biogas for exploitation of biogas derived CO2 for bioSA production and Pond A/S as user of bioSA as building block for synthesis of biopolymers applied for injection moulding. Pond, as a user of bioSA, creates the commercial pull that allows upstream valorization since they use it for a plurality of biopolymer building blocks such as poly butylene succinic acid (PBS). This includes integration of the novel production step with existing industrial process flows to validate bioSA as a precursor for multiple applications. Moreover, they will contribute to production of biomethane and PHA and to socio-economic and market analyses of the process.
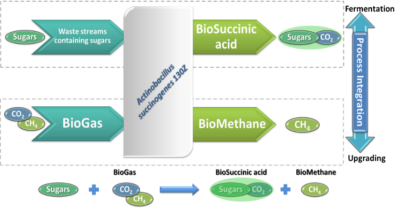
Biogas contains roughly 40% CO2, which reduces the energy density and makes the gas less suitable as energy storage/fuel compared to pure CH4. Biotechnological processes such as succinic acid fermentation requires CO2 and have thus potential for sustainable scavenging of CO2 from the biogas. The 1st generation bioSA is based on starch, while for our proposed 2nd generation bioSA, the feedstocks are waste streams such as biogas.
The main objective of CooCE is to develop, demonstrate and validate (TRL 5-6) a diverse portfolio of novel and flexible biotechnological processes for sustainable valorisation and long-term storage of CO2-rich emissions tailored to local demands. The CooCE concept includes the use of efficient and sustainable anaerobic and aerobic biological processes for the conversion of CO2 into a) biomethane, allowing flexible on-site hybrid energy storage, and b) two valuable chemical building blocks, namely biosuccinic acid (bioSA) which is a multi-use platform chemical and high-value biopolymers (polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)) for production of bioplastics. The technologies will be tested and evaluated from technical, environmental, and socio-economic perspectives, including their impact on sustainability and decarbonisation, thereby contributing to the creation of sustainable value chains in the energy and CO2 intensive industrial sectors.
The focus of the Danish partners will be to establish a cutting-edge 2nd generation CO2 conversion technology for simultaneous biomethane and bioSA production and subsequently use it for production of polymers. This offers a robust and cost-effective technology that exploits the abilities of the bacterial strain Actinobacillus succinogenes 130Z to fixate CO2 and metabolize a broad spectrum of carbohydrate sources as a high yield fermentation microbe. Pond A/S uses the bioSA for production of its biobased polymers and a key industry for Pond is the textile and apparel industry where Pond produces a substitute for polyester (PET). The Danish partners will also focus on business opportunities in upgrading of biogas into biomethane and bioSA looking into upscaled production capacity. Moreover, the Danish partners will contribute along with the other partners to develop technologies for biomethane and PHA production; and for industrial training activities, LCA assessments, and dissemination activities in the overall project.
Figur 1. Concept of bioSA and methane production from biogas and waste streams
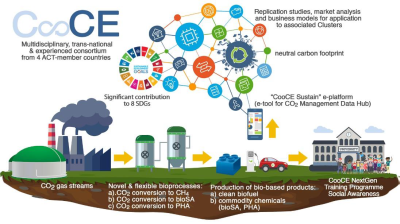
Figur 2. Overall COOCE concept showing the three implemented CO2 conversion processes.
Key figures
Category
Participants
| Partner | Subsidy | Auto financing |
|---|---|---|
| Danmarks Tekniske Universitet (DTU) | 4,24 mio. DKK | 0,47 mio. DKK |
| Lemvig Biogasanlæg Amba | 0,31 mio. DKK | 0,20 mio. DKK |
| Pond A/S | 0,28 mio. DKK | 0,12 mio. DKK |
Contact
Søltofts Plads 228A,
2800 Kongens Lyngby
Tlf.: +45 30613889


